Erosion 影像侵蝕膨脹
底下代碼,可以將文字變成較細及較粗的圖片。請注意,背影色調為黑色,效果較佳。 iterations為迭代次數,次數愈大,則明顯。

import numpy as np
import cv2
import pylab as plt
img=cv2.imread('./word.jpg')[:,:,::-1].copy()
kernel = np.ones([5,5], np.uint8)
erosion = cv2.erode(img, kernel, iterations = 1)
dilate = cv2.dilate(img, kernel, iterations = 1)
plt.subplot(131),plt.imshow(img)
plt.subplot(132),plt.imshow(erosion)
plt.subplot(133),plt.imshow(dilate)
plt.show()

角點偵測 Harris(哈里斯)
角點偵測有著極複雜的數學公式,在OpenCv只需使用cv2.cornerHarris()及cv2.dilate()及可取得
cv2.cornerHarris(src, blockSize, ksize, k, dst=None, borderType=None)
src:資料型別為 float32 的輸入影象
blockSize:角點檢測中考慮的區域大小
ksize:Sobel求導中使用的視窗大小, 3即為 3*3格
k:Harris 角點檢測方程中的自由引數,取值引數為 [0.04 0.06]
dst:輸出影象
borderType:邊界的型別
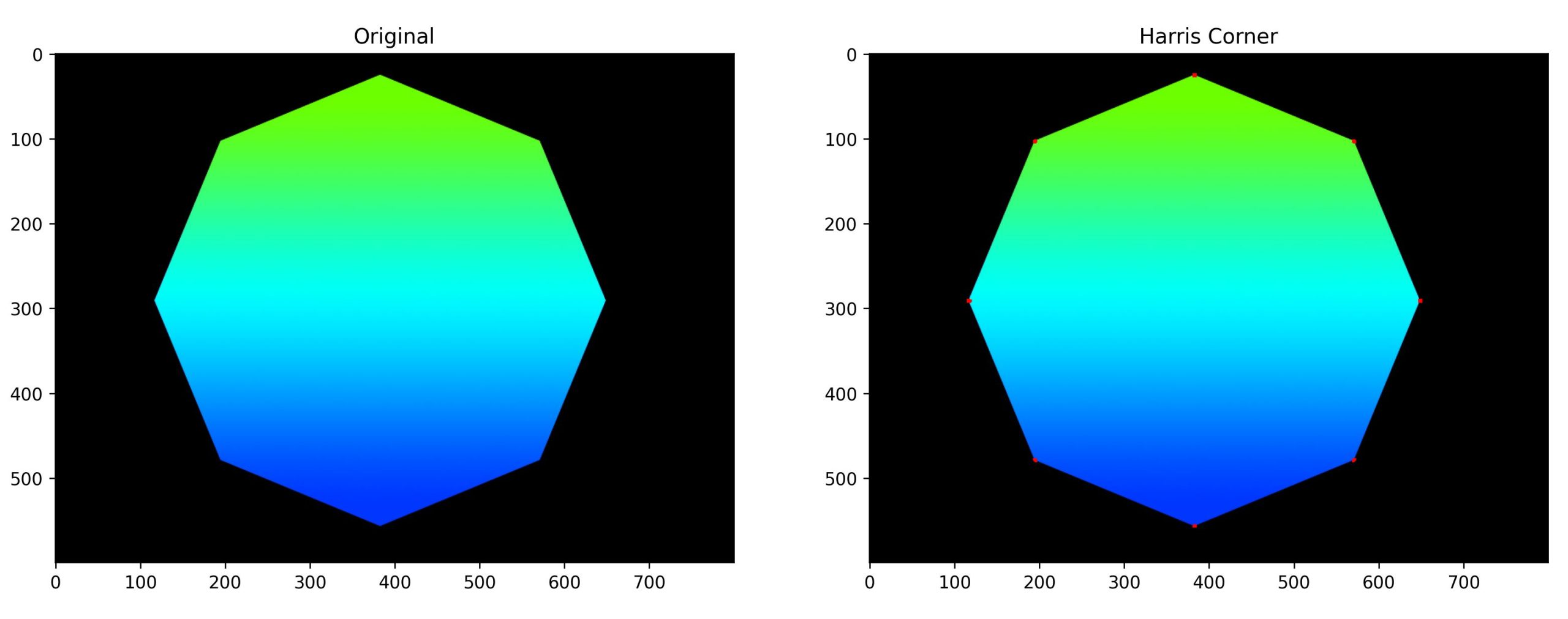
下面的代碼中,Harris_detector 為偵測到的角點資料,為一張黑底有白點的灰階圖片,再用dilate將白點放大成 dst 圖片。
import cv2
import numpy as np
import pylab as plt
filename = 'poly.jpg'
img = cv2.imread(filename)[:,:,::-1].copy()
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
#角點偵測需轉換成灰階及32位元float
gray = np.float32(gray)
detector = cv2.cornerHarris(gray, 2, 3, 0.01)
#膨脹harris結果
dst = cv2.dilate(detector, None)
print(dst.max())
# 設定閾值
thres = 0.01*dst.max()
harris=img[:].copy()
harris[dst > thres] = [255,0,0]
plt.subplot(121);plt.imshow(img);plt.title('Original')
plt.subplot(122);plt.imshow(harris);plt.title('Harris Corner')
plt.show()
Fast
Edward Rosten和Tom Drummond在2006年的論文 “用於高速拐角檢測的機器學習” 中提出了FAST(加速分段測試的特徵)算法。此法可以快速偵測出特徵點。Fast演算了最好以白底背影較為明顯。
import cv2
import pylab as plt
img = cv2.imread('poly.jpg')[:,:,::-1].copy()
#detector = cv2.FastFeatureDetector_create(threshold=40,nonmaxSuppression=True,type=cv2.FAST_FEATURE_DETECTOR_TYPE_9_16)
detector = cv2.FastFeatureDetector_create()
kp = detector.detect(img,None)
fast = cv2.drawKeypoints(img,kp,None,color=(255,0,0))
plt.subplot(1,2,1).imshow(img)
plt.subplot(1,2,2).imshow(fast)
plt.show()