網路上有另一種辨識17種花卉的討論,請先安裝如下套件
pip install tensorflow matplotlib opencv-python
收集圖片
圖片資料集請下載 flowers_17.zip,然後解開後置於專案之下。
label.txt
flowers圖片共有17種,每種 80 張圖片,所以共有1360張圖片,1~80是水仙(Narcissus),81~160是雪花蓮(Snowdrop),請先於專案下新增 label.txt,然後輸入如下資料。
1 80 Narcissus 81 160 Snowdrop 161 240 LilyValley 241 320 Bluebell 321 400 Crocus 401 480 Iris 481 560 Tigerlily 561 640 Daffodil 641 720 Fritillary 721 800 Sunflower 801 880 Daisy 881 960 ColtsFoot 961 1040 Dandelion 1041 1120 Cowslip 1121 1200 Buttercup 1201 1280 Windflower 1281 1360 Pansy
分類訓練圖片及驗証圖片
將所有的圖片分類成 train_images及 test_images二個目錄,每個目錄又有17種花卉目錄。
新增 “分割資料.py” 檔,程式碼如下。
請注意, Linux 下使用 os.listdir() 並不會依檔案字母順序列出,所以在檔案存取時的順度要特別注意。
#!./.venv/bin/python3
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
import random
import shutil
in_path="flowers_17"
train_path='train_images'
test_path='test_images'
if os.path.exists(train_path):
shutil.rmtree(train_path)
if os.path.exists(test_path):
shutil.rmtree(test_path)
os.mkdir(train_path)
os.mkdir(test_path)
files=[] #[[檔名, 花名],.....]
flowers=[] #17種花名
with open('label.txt')as file:
for line in file:
cols=line.strip().split()
s=int(cols[0])
e=int(cols[1])
flower=cols[2]
flowers.append(flower)
for i in range (s, e+1):
files.append([f'image_{i:04d}.jpg', flower])
for flower in flowers:
os.mkdir(os.path.join(train_path, flower))
os.mkdir(os.path.join(test_path, flower))
random.seed(1)
random.shuffle(files)
mid=int(len(files)*0.9)
for file, dir in files[:mid]:
source = os.path.join(in_path, file)
target = os.path.join(train_path, dir, file)
print(f'copy {source} => {target}')
shutil.copy(source, target)
for file, dir in files[mid:]:
source = os.path.join(in_path, file)
target = os.path.join(test_path, dir, file)
print(f'copy {source} => {target}')
shutil.copy(source, target)
訓練模型
建立模型跟前一篇的 5 種花卉雷同。
#!./.venv/bin/python3
import os
import cv2
from keras.src.applications.vgg19 import VGG19, preprocess_input
from keras.src.layers import GlobalAveragePooling2D, Dense, BatchNormalization, Dropout, Flatten
from keras.src.optimizers import Adam, RMSprop
from MahalSdk.cv import cv
from keras import Sequential
import pylab as plt
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
import numpy as np
with open('label.txt','r')as file:
flowers=[line.strip().split()[2] for line in file]
train_imgs=[]
train_labels=[]
test_imgs=[]
test_labels=[]
train_path="train_images"
test_path="test_images"
#製作訓練資料及測試資料
for flower in flowers:
for file in os.listdir(os.path.join(train_path, flower)):
img=cv.read(os.path.join(train_path, flower, file))[:,:,::-1].copy()
img=cv2.resize(img, (224, 224), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
train_imgs.append(img)
train_labels.append(flower)
for file in os.listdir(os.path.join(test_path, flower)):
img = cv.read(os.path.join(test_path, flower, file))[:, :, ::-1].copy()
img=cv2.resize(img, (224,224), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
test_imgs.append(img)
test_labels.append(flower)
train_imgs = np.array(train_imgs)
test_imgs = np.array(test_imgs)
#one hot
train_onehot=np.zeros([len(train_labels),17])
test_onehot=np.zeros([len(test_labels),17])
for i in range(len(train_onehot)):
train_onehot[i][flowers.index(train_labels[i])] = 1
for i in range(len(test_onehot)):
test_onehot[i][flowers.index(test_labels[i])] = 1
#建模
model_base=VGG19(weights='imagenet', include_top=False, input_shape=(224,224,3))
for layer in model_base.layers:
layer.trainable=False
model=Sequential()
model.add(model_base)
model.add(GlobalAveragePooling2D())
model.add(Dense(256,activation='relu'))
model.add(BatchNormalization())
model.add(Dense(64,activation='relu'))
model.add(BatchNormalization())
model.add(Dropout(0.2))
model.add(Dense(17, activation='softmax'))
model.compile(
optimizer=Adam(learning_rate=0.001),
#optimizer=RMSprop(learning_rate=2e-4),
loss='categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy']
)
#訓練
history=model.fit(
train_imgs,
train_onehot,
batch_size=128,
epochs=50,
validation_data=(test_imgs, test_onehot)
)
model.save("model_flower_17.keras")
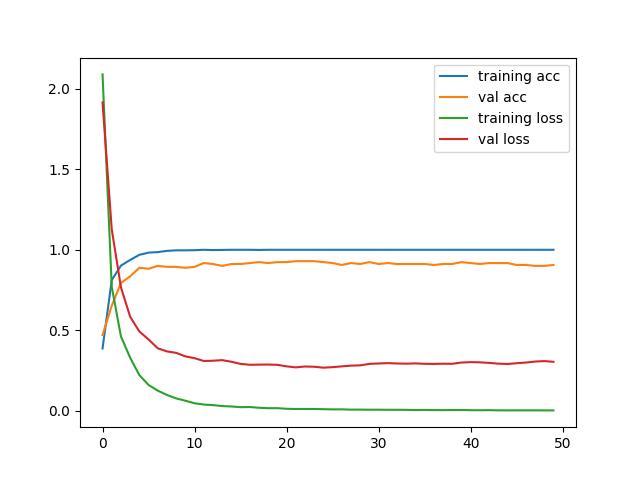
p1=plt.plot(history.history['accuracy'], label='training acc')
p2=plt.plot(history.history['val_accuracy'], label='val acc')
p3=plt.plot(history.history['loss'], label='training loss')
p4=plt.plot(history.history['val_loss'], label='val loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
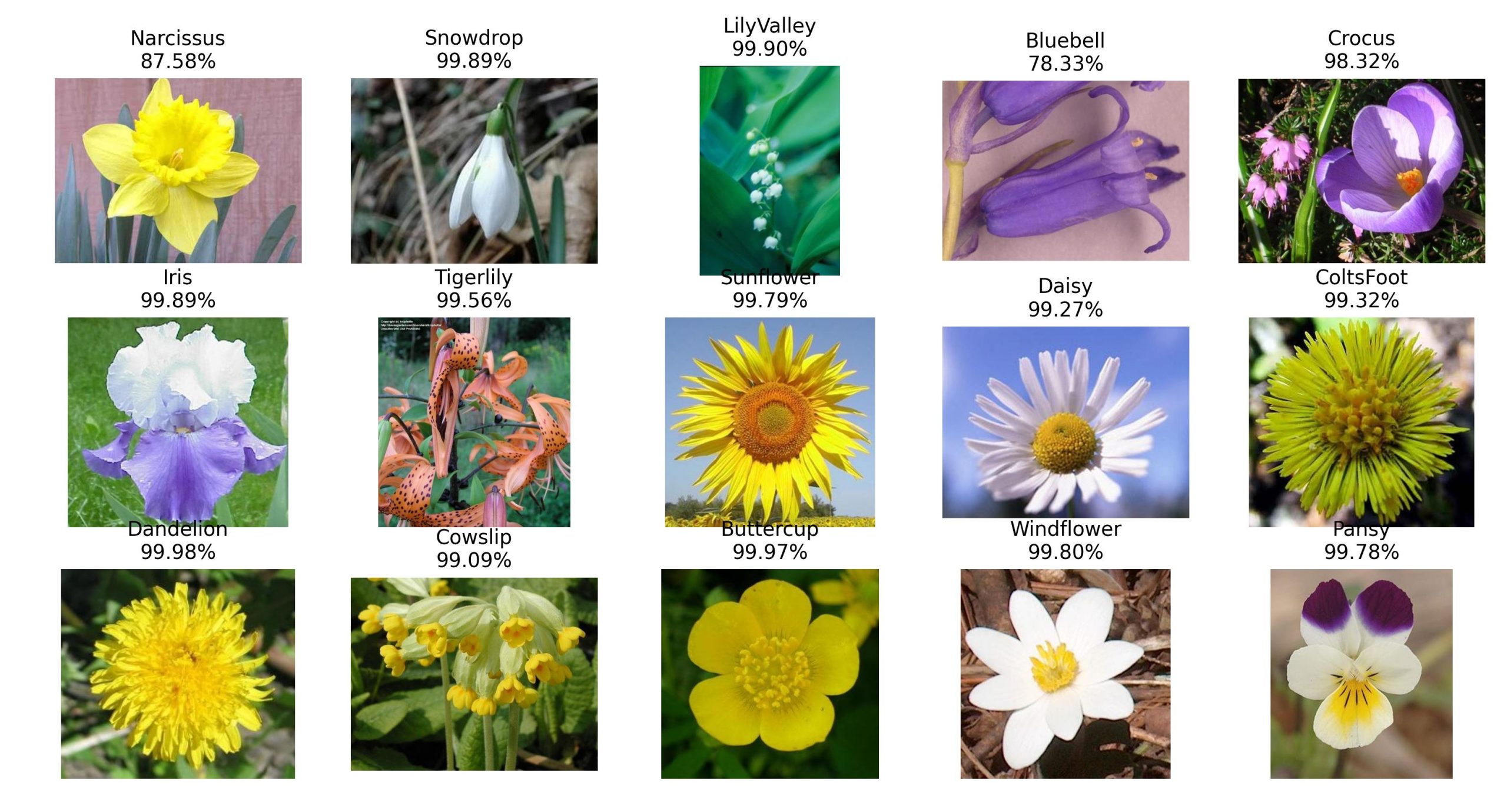
辨識圖片
上述模型若是無法訓練的話,請由如下網址下載本人已訓練好的模型
下載模型 : model_flower_17.zip
將要辨識的圖片放在 ./images裏面,然後開始辨識。
import keras
from keras.src.applications.convnext import preprocess_input
from MahalSdk.cv import cv
import cv2
import numpy as np
import pylab as plt
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
model=keras.models.load_model("./model_flower_17.keras")
path="./images"
with open('label.txt')as file:
flowers=[
line.strip().split()[2] for line in file
]
for i, file in enumerate(os.listdir(path)):
img = cv.read(os.path.join(path, file))[:,:,::-1].copy()
x = cv2.resize(img, (224, 224), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
x = np.expand_dims(x, axis=0)
x = preprocess_input(x)
out = model.predict(x)
idx=out[0].argmax()
name=flowers[idx]
score=out[0][idx]
ax=plt.subplot(3, 5, i+1)
ax.set_title(f"{name}\n{score*100:.2f}%")
ax.imshow(img)
ax.axis("off")
plt.show()

list 相加與 np.r_ 效能
上述代碼中,原本是使用 np.r_ 建立陣列,但這種方式的效能極差,所以改用 list += 來加速。由如下程式碼可知,list 相加的效能確實高出許多
import numpy as np
import time
a=[]
t1=time.time()
for i in range(1000):
a+=["hello"]*1000
a=np.array(a)
t2=time.time()
print(a)
print(f'list相加 : {t2-t1}秒')
a=np.empty(0,dtype=object)
t1=time.time()
for i in range(1000):
a=np.r_[a, ["hello"]*1000]
t2=time.time()
print(a)
print(f'np.r_ : {t2-t1}秒')
結果:
['hello' 'hello' 'hello' ... 'hello' 'hello' 'hello']
list相加 : 0.10912036895751953秒
['hello' 'hello' 'hello' ... 'hello' 'hello' 'hello']
np.r_ : 4.773515701293945秒
